
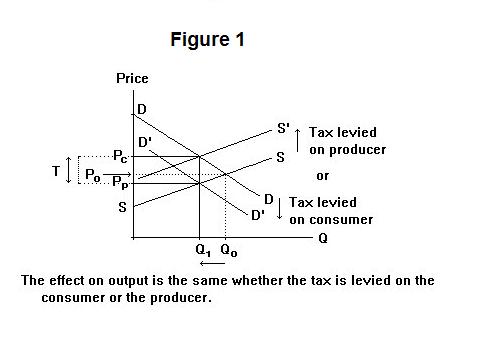
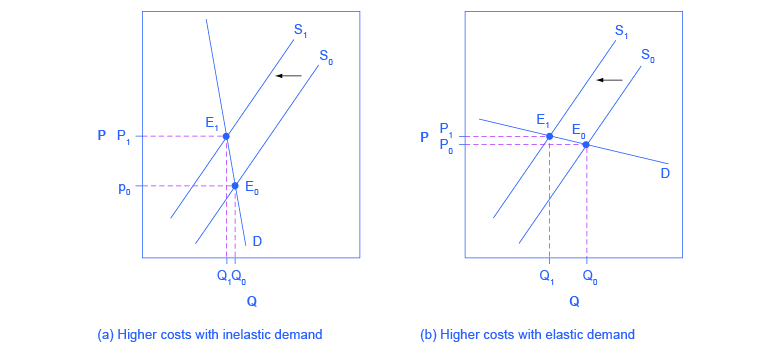
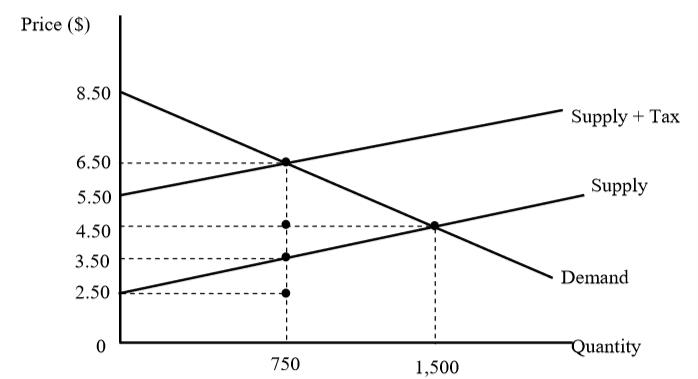
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. Effect of tax – depending on elasticity.An ad Valorem tax collects more tax from those consumers willing to purchase more expensive varieties. So those on low-income will pay a higher percentage of income in tax. The tax paid will be the same for different income groups. A specific tax increases the price of all equally and has a bigger effect on reducing overall demand. This can encourage consumers to switch from expensive alcohol and expensive cigarettes – to cheaper varieties. An ad Valorem tax places a proportionately higher tax on expensive goods.For example, cigarette tax has steadily contributed to reducing cigarette consumption in past few decades. A specific tax is effective at reducing demand.The consumers see a rise in the price of $4, and producers see a fall in the price they receive from $10 to $8. Consumers see the price rise from P1 to P2.A specific tax is borne by both producers and consumers.Placing a specific tax on a good shifts the supply curve to the left. A tax of £3.92 per 20 pack of cigarettes.Ī specific tax does not vary with the cost of the good – like for example an ad valorem tax – which is a percentage of the price.A tax of £0.40 on 500 ml sugary drinks.It is also referred to as a per-unit tax, and the tax will depend on the quantity sold (not price). An advance pricing arrangement may be unilateral involving one tax administration and a taxpayer or multilateral involving the agreement of two or more tax administrations.A specific tax is a fixed amount of tax placed on a particular good. method, comparables and appropriate adjustments thereto, critical assumptions as to future events) for the determination of the transfer pricing for those transactions over a fixed period of time. It typically includes expenses of the headquarters office and accounting expenses.ĪDMINISTRATIVE OFFICE - Office frequently located in a country other than that of the headquarters office, the parent company or country of operation.ĪDVANCE PRICING ARRANGEMENT (APA) - An arrangement that determines, in advance of controlled transactions, an appropriate set of criteria (e.g.
This is a theoretical concept and no country uses it.ĪCCOUNTING PERIOD - A period of time used by taxpayer for the determination of tax liabilityĪCCOUNTS PAYABLE - A list of the debts currently owed by a person or business, mainly for the purchase of services, inventory, and suppliesĪCCOUNTS RECEIVABLE - A list of the money owed on current account to a creditor, which is kept in the normal course of the creditor's business and represents unsettled claims and transactionsĪCCOUNTING RECORDS - All documents and books used in the preparation of the tax return and all financial statements, including general ledger, subsidiary ledgers, sales slips, and invoices.ĪCCRUAL BASIS (ACCRUAL METHOD) - An accounting method whereby income and expense items are included in taxable income or expense as they are earned or incurred, rather than when they are received or paidĪD VALOREM TAX - A tax on goods or property expressed as a percentage of the sales price or assessed valueĪDMINISTRATIVE COMPANY - See: Service companyĪDMINISTRATIVE EXPENSES - Expenses that are not as easily associated with a specific function as are the direct costs of manufacturing and selling. In respect of VAT, tax would be computed as a percentage levy on the excess of sales over purchases. They are not considered to necessarily reflect official position of the OECD in interpreting international tax terms, for example, in the tax treaty context.Ī- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- ZĪBATEMENT - A reduction in the assessment of tax, penalty or interest when it is determined the assessment is incorrectĪBUSE OF LAW - The doctrine which allows the tax authorities to disregard a civil law form used by the taxpayer which has no commercial basisĪCCELERATED DEPRECIATION - Method of depreciation under which taxpayers may allocate larger depreciation deductions to the first year or first few years of useful business assets, such as plant and machineryĪCCOUNTING BASIS - Method of calculating amounts subject to income tax and VAT.
Green growth and sustainable developmentĭisclaimer: Explanations on the terms are very condensed and may not be complete.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
